L-Methionine Powder
Other Names:selenium methionine
Purity:99%L-Methionine
Test Method:HPLC
Appearance:White powder
CAS No.:63-68-3
OEM service:Supply the OEM bag and OEM bottle and formula
Certifications: GMP, ISO9001:2015, ISO22000:2018, HACCP, KOSHER and HALAL.
MOQ: 1KG
Sample: Free sample available
Production Capacity: 1000KG/month
Delivery Time: Delivery within one day from the warehouse
Shelf Life: 2 years
Payment: T/T
Company Advantage:100,000 level clean production workshop, Non-additive, Non-GMO, Non-Irradiated/treated by heat only
- Fast Delievery
- Quality Assurance
- 24/7 Customer Service
Product Introduction
What is L-Methionine?
L-Methionine is an essential amino acid for animals that cannot be synthesized in the body and must be obtained from feed. It effectively promotes animal growth, improves feed conversion ratio, enhances immune function, and can be used for hair development. In livestock farming, it is widely added to pig, poultry, and aquatic feeds to compensate for insufficient levels in basic raw materials (such as corn-soybean meal) and improve farming efficiency.

Healthkintai® is a leading L-Methionine manufacturer and supplier in China. If you need 99%L-Methionine, please contact us at info@kintaibio.com.
L-Methionine Specifications
|
Product name |
CAS No. |
Specifications |
|
L-Methionine |
63-68-3 |
99%L-Methionine |
|
DL-Methionine |
59-51-8 |
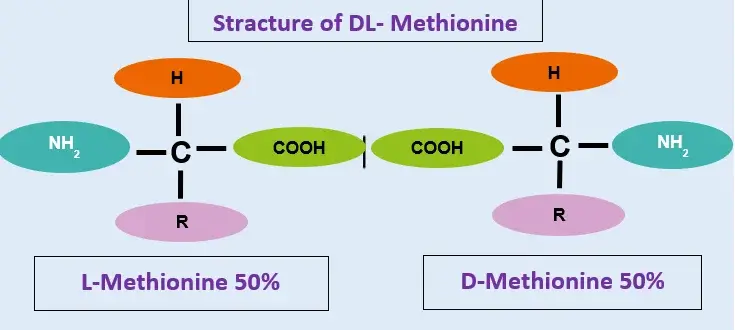
99%DL-Methionine (D-Methionine:L-Methionine=1:1) |
Sample available! Contact us now>>>
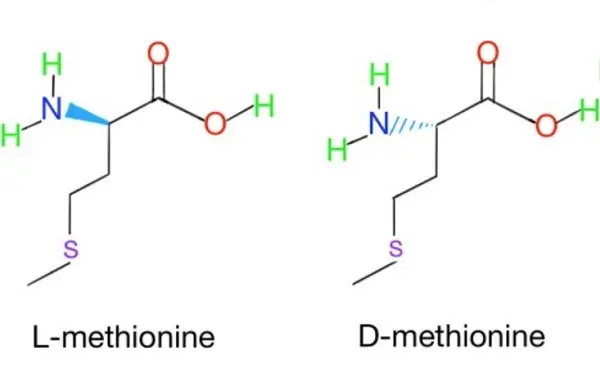
Difference between DL-Methionine and L-Methionine
DL-methionine is a synthetically produced 1:1 mixture of D- and L-methionine forms, offering low cost and making it a mainstream additive in the feed industry. L-methionine is a naturally occurring, single levorotatory isomer that can be directly and efficiently utilized by the body.
Their core differences lie in their structure and activity. The DL-methionine is a racemic mixture with lower biological activity; the L-methionine is the naturally occurring active form. Their bioavailability also differs significantly, with the overall utilization rate of the DL-methionine (approximately 80-90%) lower than that of pure L-methionine (100%). Due to its chemical synthesis, the DL-methionine is significantly cheaper than L-methionine produced through bio-fermentation.
Their application scenarios are drastically different:
- DL-methionine is used in cost-effective livestock, poultry, and aquatic feeds.
- L-methionine is used in pharmaceutical injections, high-end health supplements, pet food, and specialized medical nutritional products, requiring high purity and direct biological activity.
L-methionine Benefits
1. L-Methionine Effects on Sleep
L-Methionine indirectly influences sleep rhythms by participating in the synthesis of neurotransmitters and hormones. It is a key raw material for the synthesis of serotonin, an important neurotransmitter, which can be further converted into melatonin, a hormone that regulates the sleep-wake cycle. Theoretically, sufficient L-methionine may support the normal functioning of this pathway. Currently, there is a lack of high-quality human clinical studies directly confirming that L-methionine supplementation improves sleep in ordinary people. Its effects are more likely related to correcting specific deficiency states or supporting overall neurological health, rather than acting as a direct "sleep aid."

2. Supportive Effects on Hair Health
This is one of the most clearly defined and direct effects of L-methionine, stemming from its sulfur-containing amino acid nature. The main component of hair is keratin, and sulfur is a key element in the formation of disulfide bonds within keratin (determining hair strength and elasticity). L-methionine is an important source of cystine and sulfur in the body. In animal husbandry (especially for pet coat care) and some hair care products, supplementation with L-methionine or its active form in the body (such as cystine) has been shown to help improve hair strength, shine, and growth quality.

3. L-methionine for Weight Management
Its effect is not a direct "weight loss," but rather it is achieved by influencing metabolic pathways. As a precursor to S-adenosylmethionine, it provides methyl groups for phospholipid synthesis (such as lecithin), supports hepatic fat metabolism, and may help prevent abnormal fat accumulation in the liver. As a precursor to the synthesis of certain neurotransmitters, it may theoretically indirectly affect appetite regulation, but this effect is very indirect and varies greatly from person to person.

4. Liver Protection
L-methionine's protective effect on the liver is primarily achieved through its dual role as a key metabolic precursor. First, it is an essential raw material for the synthesis of glutathione, a core antioxidant and detoxifying agent in the liver, directly neutralizing free radicals and metabolizing drug and alcohol toxins, thus protecting hepatocytes. Second, it is converted into S-adenosylmethionine in the body, providing the necessary methyl group for hepatic fat metabolism, promoting phospholipid synthesis, and helping to prevent and reduce abnormal fat accumulation in the liver, maintaining normal liver function. Based on this mechanism, it is used clinically as an adjunct treatment for specific types of drug-induced liver injury, such as acetaminophen poisoning.
L-methionine Uses
1. Animal Nutrition and Feed Industry
As an essential amino acid, it is mainly used to balance feed formulations. In pig, poultry, and aquaculture, supplementing with L-methionine or its economical alternative, DL-methionine, can precisely compensate for the amino acid deficiencies in corn-soybean meal-based basal feeds, significantly improving feed conversion ratio, promoting animal growth, increasing lean meat percentage and egg production. It is a key nutrient for achieving cost reduction and efficiency improvement in modern intensive farming.

2. Medicine and Human Health
In the pharmaceutical field, high-purity L-methionine supplement is mainly used as an adjunct treatment for liver diseases. As a precursor to glutathione, it is used to assist in the treatment of drug-induced liver injury such as acetaminophen poisoning, helping the liver detoxify. Nutritional support, as a basic component of amino acid infusions and complete nutritional preparations, provides essential nutrients for patients who cannot eat orally or have specific deficiencies.

3. Cosmetics and Personal Care
Its derivatives (such as acetylmethionine) are used in skincare and haircare products. Its primary function is to provide sulfur, a raw material for the synthesis of key proteins in skin and hair (such as keratin and collagen), and it is claimed to help strengthen hair resilience and improve skin barrier function. This application leverages its fundamental role in structural synthesis.

L-Methionine Dosage
|
Application Field |
Target / Purpose |
Typical Dosage Range & Form |
Key Considerations & Notes |
|
Human Dietary Supplement |
General health / potential support |
500 - 1500 mg per day, often divided. Form: Pure L-Methionine capsules or powder. |
Crucial: NOT recommended for self-supplementation without medical supervision. Excess can elevate homocysteine (a cardiovascular risk factor) and disrupt amino acid balance. Always consult a doctor. |
|
Clinical / Medical Use |
Treatment of specific conditions (e.g., acetaminophen poisoning, liver support) |
Determined by a physician. Can range from 2 to 8 grams per day (or more) in divided doses under strict monitoring. |
Used in hospitals or clinical settings. Dosage is highly individualized based on body weight, condition severity, and blood tests (e.g., homocysteine, liver enzymes). |
|
Animal Nutrition (Feed Additive) |
Poultry (broilers/layers), Swine, Aquaculture |
Varies significantly (0.05% - 0.3% of total feed), commonly expressed as added 0.5 to 3.0 kg per metric ton of feed. |
Dosage is precisely calculated by nutritionists based on species, growth stage, and basal diet composition (e.g., corn-soybean meal). The more common source in feed is DL-Methionine for cost efficiency. |
|
Cosmetic / Topical Use |
Skin care, hair care products |
0.1% - 2% concentration in the final product formulation. Form: Often used as acetylated derivatives (e.g., Acetyl Methionine). |
Used as a functional ingredient to provide sulfur for keratin/collagen synthesis. Considered safe at these low topical concentrations. |
Interested? Contact us to get more details>>>
Side Effects of L-Methionine
L-Methionine is generally safe when consumed through food, but supplementation, especially at high doses, carries risks. The most significant side effect is the elevation of homocysteine levels in the blood, which is a known independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Other potential adverse effects include gastrointestinal discomfort (such as nausea and diarrhea), acidosis (increased acidity in bodily fluids) in individuals with impaired kidney function, and in rare cases of extreme excess, it may contribute to neurological symptoms. It is contraindicated for patients with homocysteinuria, severe liver disease, or certain metabolic disorders. Therefore, unsupervised supplementation is strongly discouraged.

Why Choose KINTAI L-Methionine?
- We are a leading L-Methionine manufacturer in China, with a large scale production plant and a professional R&D team, capable of providing you with 99% pure L-Methionine.
- We hold multiple international authoritative certifications, including GMP, ISO9001:2015, ISO22000:2018, HACCP, KOSHER, and HALAL, ensuring the quality of our products.
- We can flexibly customize products for you, such as concentration and dosage form, perfectly meeting your requirements, and provide OEM & ODM services.
- If you need 99% L-Methionine Powder, please feel free to contact us at info@kintaibio.com.
FAQ
Q1:Is L-methionine good for hair?
A1:Yes, L-methionine plays a vital role in supporting hair health, primarily as a key raw material. It is a sulfur-containing amino acid and a major precursor in the body for the synthesis of cystine, a core building block of keratin, the main component of hair. The disulfide bonds (formed by sulfur) within keratin directly determine hair strength, elasticity, and shine. Therefore, sufficient L-methionine is an essential physiological basis for normal hair growth, strength, and shine.
Q2:Who should not take L-methionine?
A2:Patients with specific conditions: This supplement is contraindicated in patients with hyperhomocysteinemia, homocystinuria, severe liver or kidney dysfunction, or metabolic acidosis, as it may directly worsen their condition. Special physiological stages: Pregnant women, breastfeeding women, and children should not supplement without medical advice due to insufficient safety data. Individuals with adequate diets: For healthy individuals who obtain sufficient methionine from their daily diet, additional supplementation is not only unnecessary but may also increase cardiovascular risk and disrupt amino acid balance due to excessive intake.
Q3:L-methionine vs L-theanine which is better?
A3:There is no absolute "better"; the choice depends on your goals: L-methionine is an essential amino acid whose core function is to serve as a raw material for the synthesis of proteins and many key metabolites (such as glutathione), and it is crucial for physiological foundations such as liver detoxification and hair health. L-theanine is a non-essential amino acid, mainly found in tea, and its core function is to regulate neurotransmitters in the brain, helping to relax emotions, relieve anxiety, and potentially improve concentration, without affecting sleep.
Our Certifications

Send Inquiry


_1765163964747.webp)