Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC) Powder
Specification: 98% Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC)
Appearance: White powder
Test Method: HPLC
Origin: China
Lead time:1-3 days
Storage: Cool dry place and avoid light
Shelf Life: 2 years
MOQ: 1KG
Sample: Free sample available
Certs: GMP, ISO9001:2015, ISO22000:2018, HACCP, KOSHER, HALAL
Advantage: 100,000 level clean production workshop, Non-additive, Non-GMO,
radiationless qualified product.
- Fast Delievery
- Quality Assurance
- 24/7 Customer Service
Product Introduction
Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC) Supplier
Healthkintai® specializes in manufacturing 98% Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC) powder.
NHDC is a high-intensity functional sweetener produced through safe processes. Its core commercial value lies in its exceptional sweetness and outstanding bitterness-masking function, making it a premium raw material for enhancing product taste, developing low-sugar/sugar-free healthy foods, and specific formulations (such as pharmaceutical flavoring).
Reference: https://www.scribd.com/document/355657666/Neohesperidin-dihydrochalcone
If you require high-quality 98% Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC) powder, please feel free to contact us at health@kintaibio.com.
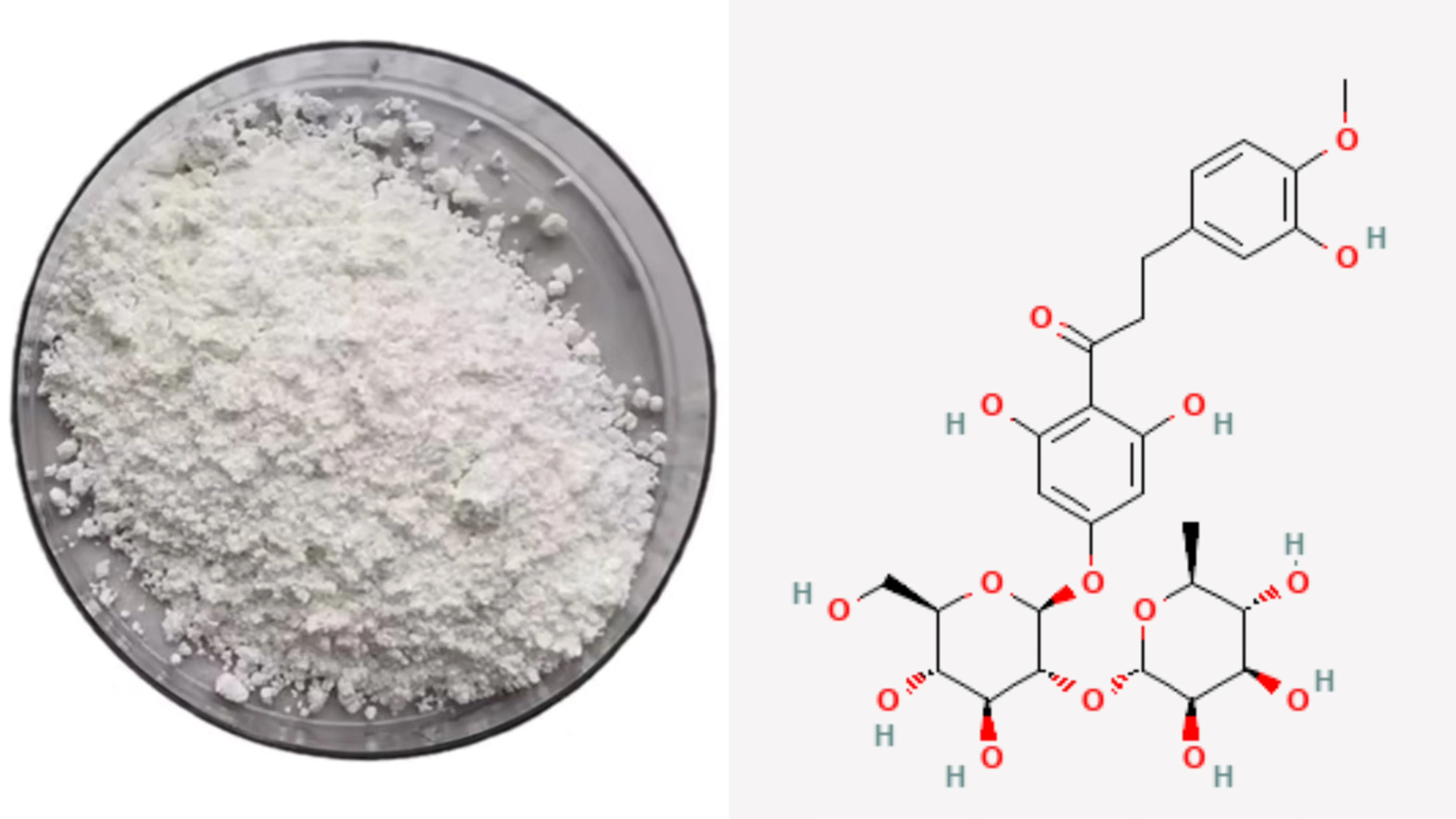
Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone (NHDC) powder and structure
The Technical Data Sheet (TDS) of Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC) Powder
|
Item |
Specification |
Testing method |
|
Purity |
98% Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC) |
HPLC |
|
Appearance(Color) |
White powder |
Organoleptic |
|
Loss on drying |
3.49% |
USP<731> |
|
E.Coli |
Negative |
GB 4789.3 |
|
Salmonella |
Negative |
GB 4789.4 |
|
Heavy Metals (Total) |
≤10.0ppm |
GB 2762-2025/ICP-MS |
|
Arsenic(As) |
≤ 1.0ppm |
GB 2762-2025/ICP-MS |
|
Lead(Pb) |
≤ 3.0ppm |
ICP-MS |
|
Mercury(Hg) |
≤ 0.1ppm |
ICP-MS |
|
Cadmium(Cd) |
≤ 1.0ppm |
ICP-MS |
Regulatory Status of Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC)
NHDC is widely approved globally as a flavor enhancer and sweetener.
Safety
NHDC is non-mutagenic, non-carcinogenic, non-cariogenic, and has no significant toxic effects. It has no adverse effects on the body and is metabolized rapidly.
Regulatory Approval
United States (FDA)
Status: GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) for use as a sweetener and flavor enhancer in various foods.
Details: A 2020 no-objection letter confirmed its GRAS status, allowing use up to 10-1000 ppm.
European Union (EFSA)
Status: Approved food additive (E-959) and flavouring (FL-16.061).
Details: Re-evaluated by EFSA in 2022, maintaining its safety with an established ADI of 20 mg/kg body weight.
Reference
https://www.fda.gov/media/144168/download
https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2444
Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC) Solubility
The solubility characteristics of NHDC are as follows:
Water Solubility
NHDC is almost insoluble in water at room temperature, but its solubility increases significantly under heated conditions. For example, it can dissolve in hot water at 45℃, and its solubility reaches 653 g/L at 80℃. This property makes it more widely applicable in food and beverage products that undergo high-temperature processing, such as hot drinks and baked goods.
Solubility in Organic Solvents
NHDC is readily soluble in polar organic solvents, such as dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and methanol, which provides convenience for laboratory research or specific industrial applications. Meanwhile, it is almost insoluble in non-polar solvents, such as dichloromethane, diethyl ether, and benzene, further limiting its use in certain non-polar systems.
Temperature Dependence
The solubility of NHDC increases significantly with rising temperature. For instance, its solubility is only 0.2 g/L at 20℃, but it reaches 653 g/L at 80℃. This temperature sensitivity necessitates consideration of processing temperature on dissolution effects during formulation design.
Sample available! Contact us to get more details. >>>
Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC) Uses
Food Industry
Sweetener: As a low-energy food sweetener, NHDC is widely used in over 30 categories of food products, including fruit juices, candies, pastries, and frozen dairy products, providing sweetness and reducing production costs.
Bitterness Masking Agent: Below its sweetness threshold, NHDC acts on bitterness receptors, raising the human threshold for bitterness and demonstrating superior bitterness masking effects compared to ordinary sweeteners.
Flavor and Fragrance Synergist: NHDC has a fragrance profile similar to maltol and ethyl maltol, and can produce significant synergistic effects with them, enhancing the flavor of food products and increasing the intensity and persistence of aroma.
Feed Industry
Sweetener (Flavor Corrector): Adding NHDC to feed can increase egg production rates in laying hens, improve intestinal health, and serve as a sweetener in starter feeds for young livestock, stimulating appetite and promoting growth in piglets.
Synergistic Enhancement: When combined with saccharin sodium, the sweetness of NHDC can increase by over 40%. This combination not only masks the aftertaste of saccharin sodium but also results in a purer sweetness.
Reference: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1756464624001208
Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical Flavor Corrector: NHDC is commonly used in pharmaceutical formulations as a sweetener (flavor corrector) to improve the taste of medications, particularly pediatric drugs and oral preparations, thereby enhancing patient compliance.
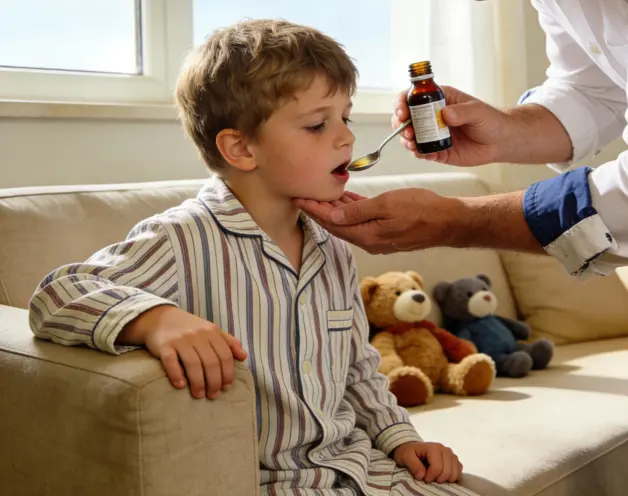

Functional Food Ingredient: Due to its low-calorie properties, NHDC is suitable for use in functional foods and dietary supplements as a sugar substitute, meeting the dietary needs of specific populations.
Biomedical Research
1. NHDC-bovine serum albumin conjugate (NHDC-BSA) can be used as an antigen to immunize animals for antibody production. This conjugate can also be coated onto solid supports for the detection of NHDC and its antibodies.
2. NHDC can also function as a stabilizer, carrier, etc., in biomedical research.
Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC) in Skincare
Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone (NHDC) can boast dual skincare benefits for both topical and oral use.
When applied topically, it exerts potent antioxidant effects by scavenging free radicals and inhibiting lipid peroxidation, helping fend off photoaging and environmental aging to reduce fine lines and enhance skin firmness. Meanwhile, it can suppress inflammatory signaling pathways and promote ceramide synthesis to alleviate redness and itching in sensitive skin and repair damaged skin barriers. Additionally, it enhances the moisture-retention capacity of the stratum corneum by absorbing moisture and regulating aquaporins, improving skin dryness.
When taken orally, it can enhance the body’s overall antioxidant capacity through the bloodstream, increase skin moisture content and UV resistance, and improve skin texture from the inside out. With high safety, it is suitable for anti-aging, soothing, and moisturizing skincare products as well as oral beauty supplements.
Referance: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17268074/
Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC) Side Effects
Oral administration is the primary application scenario of NHDC (e.g., health supplement capsules, sugar-free foods). Its side effects are mainly related to “dosage” and “individual digestive sensitivity,” with an extremely low incidence rate:
At the Recommended Daily Dosage (in line with ADI: 0-5 mg/kg body weight/day)
Rare mild digestive system reactions: Only a tiny number of people with weak digestive functions (e.g., the elderly, children) may experience transient mild discomfort, including:
Abdominal distension and mild abdominal flatulence (because part of NHDC is not fully absorbed in the intestines, which may slightly stimulate intestinal peristalsis);
Occasional loose stools (incidence rate < 1%, no risk of diarrhea, and symptoms relieve immediately after discontinuing use).
In Case of Overdosage (far exceeding the ADI, e.g., >1000 mg per day)
Potential digestive system burden: May aggravate intestinal discomfort, manifested as persistent abdominal distension and increased frequency of defecation (but there is no risk of dehydration or electrolyte imbalance);
No reports of severe toxicity: Even in acute animal toxicity tests (single oral dose of 5000 mg/kg body weight in rats), no severe toxic reactions such as death or organ damage were observed—only short-term loss of appetite (recovered within 24 hours) was noted, proving its "extremely low acute toxicity."
Why Should You Buy Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC) Powder from Healthkintai®?
Healthkintai® is a professional supplier of high quality ingredients which based in Shaanxi province, China. It was established by group of experts who have more than ten years experiences.
If you want to order high-quality 98% Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone(NHDC) powder, please contact us at health@kintaibio.com.
We have regular factory inspection to view the production status. And compare all qualified batches to select the best one for our customer before delivery. We always put the interests of our customers first and aim to improve customer value.
FAQ
1. What’s the difference between NHDC with other sweeteners?
NHDC stands out as a natural, high-intensity sweetener from citrus with exceptional heat/pH stability, a slow sweetness onset and lingering aftertaste (like licorice), and powerful synergistic effects, boosting other sweeteners (like aspartame, stevia) and masking off-flavors, making it great for cost savings and flavor enhancement in various foods, unlike simpler sugars or some artificial sweeteners that lack this stability or synergy, though its intense licorice note requires careful formulation.
2. What are the two broad classes of sweeteners?
The two broad classes of sweeteners are Nutritive Sweeteners (which provide calories/energy like sugar, fructose, honey) and Non-Nutritive Sweeteners (NNNS, also called sugar substitutes or artificial sweeteners, which offer intense sweetness with few or no calories, like aspartame, stevia, or monk fruit). Some classify sugar alcohols (like xylitol, erythritol) as a separate nutritive group or within nutritive sweeteners, while others group low-calorie sweeteners (LCS) with NNS.

Send Inquiry




_1765531293510.webp)