What is the difference between astaxanthin and vitamin C?
2025-05-16 09:43:02
When comparing powerful antioxidants in the realm of health supplements, astaxanthin and vitamin C frequently emerge as frontrunners, yet they possess distinctly different properties and benefits. In the ongoing astaxanthin vs vitamin C debate, understanding their unique characteristics is essential for making informed health decisions. Astaxanthin, a carotenoid pigment found primarily in marine organisms like Haematococcus pluvialis algae, offers exceptional antioxidant capacity that surpasses many other natural compounds, including vitamin C. While vitamin C has long been celebrated for immune support and collagen production, astaxanthin's molecular structure allows it to protect both water-soluble and fat-soluble parts of cells, making it uniquely versatile in combating oxidative stress throughout the body.
Molecular Structure and Antioxidant Mechanisms
The fundamental differences between astaxanthin and vitamin C begin at the molecular level, which explains their varying effects on human health.
Chemical Properties That Define Effectiveness
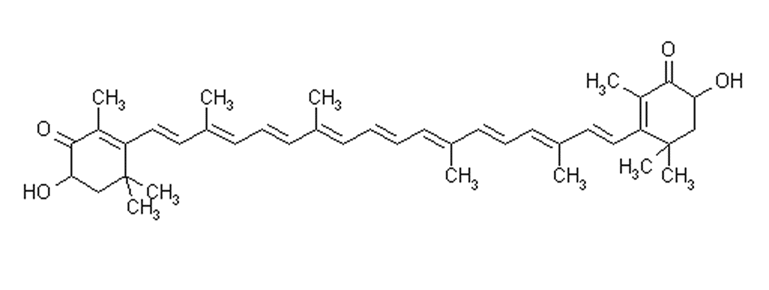
Astaxanthin's unique molecular structure features a long carbon chain with hydroxyl and keto groups at each end, giving it both lipophilic (fat-loving) and hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. This amphipathic nature allows astaxanthin to span cell membranes, protecting both the water-soluble and fat-soluble portions of cells from oxidative damage. In contrast, vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is exclusively water-soluble, limiting its protective capacity to aqueous environments within the body. When evaluating astaxanthin vs vitamin C, this difference in solubility significantly impacts where and how these antioxidants function in the human body. KINTAI Biotech's Natural Astaxanthin Powder, derived from Haematococcus pluvialis, harnesses these unique chemical properties in their purest form, free from artificial and chemical components, making it an exceptionally valuable health ingredient for comprehensive cellular protection.
Potency Comparison in Neutralizing Free Radicals
Scientific research has consistently demonstrated astaxanthin's superior antioxidant capacity compared to vitamin C and other antioxidants. Studies indicate that astaxanthin can be up to 6,000 times more potent than vitamin C in neutralizing certain types of free radicals. This remarkable potency stems from astaxanthin's unique ability to donate electrons without becoming a pro-oxidant itself, unlike vitamin C which can sometimes generate free radicals after neutralizing others. In the astaxanthin vs vitamin C comparison, this distinction is crucial for long-term antioxidant therapy. KINTAI's high-specification astaxanthin (available in 1%-10% concentrations) maximizes this potency advantage through careful extraction processes that preserve the carotenoid's natural strength, helping to combat oxidative stress more effectively than conventional antioxidants like vitamin C.
Stability and Bioavailability Factors
Another significant difference between astaxanthin and vitamin C lies in their stability and bioavailability profiles. Vitamin C is notoriously unstable, easily degrading when exposed to heat, light, and oxygen. Its water solubility also means it's quickly excreted from the body, requiring frequent replenishment. Conversely, astaxanthin demonstrates remarkable stability under various environmental conditions and has a longer half-life in the body due to its lipophilic properties. In the astaxanthin vs vitamin C discussion, this translates to potentially longer-lasting antioxidant protection from astaxanthin. KINTAI Biotech ensures maximum stability of their Natural Astaxanthin Powder through careful storage recommendations (cool, dry place, avoiding light) and specialized processing techniques, resulting in a product with a two-year shelf life while maintaining optimal bioactivity—a significant advantage over the typically shorter shelf life of vitamin C products.
Health Benefits and Applications
Beyond their antioxidant properties, astaxanthin and vitamin C offer distinct benefits that make them valuable for different health applications.
Skin Health and Anti-Aging Effects
When comparing astaxanthin vs vitamin C for skin health, both offer significant benefits but through different mechanisms. Vitamin C is well-known for its role in collagen synthesis, which helps maintain skin elasticity and promotes wound healing. However, astaxanthin offers comprehensive skin protection that extends beyond vitamin C's capabilities. As outlined in KINTAI's product information, astaxanthin can pass through the skin's layers more effectively due to its lipophilic properties, providing deeper protection against UV damage and photo-aging. It simultaneously reduces wrinkles, combats age spots, and improves skin elasticity and moisture retention. Unlike vitamin C, which primarily works on collagen production, astaxanthin's moisturizing effect improves overall skin health and appearance from multiple angles. KINTAI's Natural Astaxanthin Powder, with its high purity and potency, delivers these benefits without artificial additives, making it an ideal ingredient for premium anti-aging cosmetic formulations.
Inflammatory Response Regulation
Both astaxanthin and vitamin C possess anti-inflammatory properties, but they work through different pathways. Vitamin C primarily reduces inflammation through its antioxidant effects and by promoting immune cell function. Astaxanthin, however, demonstrates more comprehensive anti-inflammatory action by inhibiting multiple inflammatory mediators and signaling pathways. In studies comparing astaxanthin vs vitamin C, astaxanthin has shown superior ability to reduce inflammatory markers related to chronic conditions. KINTAI's Natural Astaxanthin Powder leverages these properties to offer significant anti-inflammatory benefits that complement its antioxidant effects. This dual action makes it particularly valuable for conditions where chronic inflammation plays a key role, including arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and various autoimmune disorders. The pure, natural source of KINTAI's astaxanthin ensures that these anti-inflammatory benefits are delivered without the synthetic additives found in some vitamin C supplements.
Immune System Enhancement and Protection
Vitamin C has long been celebrated for its immune-boosting properties, particularly in preventing and reducing the duration of the common cold. Astaxanthin offers complementary but distinct immune benefits. While vitamin C primarily supports neutrophil function and enhances epithelial barriers, astaxanthin modulates immune response by balancing both innate and adaptive immunity. In the astaxanthin vs vitamin C comparison for immune function, astaxanthin demonstrates particular strength in enhancing natural killer cell activity and T-cell response, which are crucial for fighting infections and abnormal cells. KINTAI Biotech's GMP-certified astaxanthin production ensures their Natural Astaxanthin Powder maintains optimal immune-enhancing properties. As stated in their product information, astaxanthin's ability to combine with skeletal muscle allows it to effectively remove exercise-generated free radicals in muscle cells, strengthening metabolism and enhancing overall immunity in ways that vitamin C cannot match.

Specific Applications and Industry Uses
The distinct properties of astaxanthin and vitamin C lead to different applications across various industries.
Nutraceutical and Dietary Supplement Formulations
In the world of dietary supplements, the astaxanthin vs vitamin C comparison reveals complementary roles rather than competing ones. Vitamin C predominantly appears in immune-supporting formulations and general multivitamins due to its water-soluble nature and essential vitamin status. Astaxanthin, with its superior antioxidant capacity, typically features in premium anti-aging, sports performance, and comprehensive antioxidant formulations. KINTAI Biotech leverages their expertise in herbal extracts to produce Natural Astaxanthin Powder that meets the highest industry standards, including ISO9001:2015, ISO22000:2018, HACCP, KOSHER, and HALAL certifications. Their ability to customize astaxanthin concentrations from 1% to 10% allows supplement manufacturers to create targeted formulations addressing specific health concerns that vitamin C alone cannot adequately address. This flexibility, combined with KINTAI's OEM and ODM services, enables clients to develop distinctive astaxanthin products tailored to various consumer segments and health needs.
Cosmetic and Skincare Product Development
When formulating skincare products, choosing between astaxanthin vs vitamin C depends on the desired benefits and formulation requirements. Vitamin C is a skincare staple for brightening and collagen stimulation but presents significant formulation challenges due to its instability and oxidation potential. Astaxanthin offers distinctive advantages for premium skincare products, including superior photo-protection, deep penetration into skin layers, and exceptional stability in various formulation types. KINTAI's Natural Astaxanthin Powder provides cosmetic manufacturers with a versatile ingredient that remains stable in creams, serums, oils, and masks—a significant advantage over notoriously unstable vitamin C. The natural origin from Haematococcus pluvialis ensures KINTAI's astaxanthin meets the growing consumer demand for clean beauty ingredients while delivering potent anti-aging benefits through multiple pathways. Through their comprehensive product development services, KINTAI assists partners in creating innovative skincare formulations that capitalize on astaxanthin's unique properties beyond what vitamin C can offer.
Food, Beverage, and Animal Feed Applications
The applications of astaxanthin vs vitamin C in food, beverage, and animal nutrition sectors highlight their distinctive properties. Vitamin C primarily serves as a nutritional fortification ingredient and preservative in food products, while astaxanthin offers both functional benefits and natural coloration. KINTAI's Natural Astaxanthin Powder has gained significant traction in premium functional beverages, where its stability advantages over vitamin C prevent degradation during processing and storage. In the aquaculture industry, astaxanthin serves functions that vitamin C cannot match—enhancing the vibrant coloration of salmon, shrimp, and ornamental fish while improving their overall health and stress resistance. As outlined in KINTAI's product information, their astaxanthin improves the vitality of crustaceans, enhances immune function, and provides a brightening effect that increases the market value of farmed species. With KINTAI's stringent quality controls ensuring their astaxanthin meets international standards for purity and efficacy, food producers and aquaculture operations can incorporate this powerful carotenoid with confidence in both its safety and performance advantages over traditional antioxidants like vitamin C.

Conclusion
In the astaxanthin vs vitamin C comparison, both offer significant health benefits, but astaxanthin's unique molecular structure, superior antioxidant potency, and distinctive applications give it advantages in many contexts. While vitamin C remains essential for human health, astaxanthin's exceptional properties make it an invaluable complement in comprehensive health and beauty regimens.
Are you interested in incorporating premium Natural Astaxanthin Powder into your product formulations? KINTAI Biotech offers complete professional solutions from concept development to regulatory compliance, with customizable OEM and ODM services that meet your specific requirements. Our GMP-certified, ISO-standardized production ensures the highest quality natural astaxanthin for applications ranging from nutraceuticals to cosmetics. Contact us today at info@kintaibio.com to discover how our expertise in herbal extracts can enhance your product offerings.
References
1. Fassett RG, Coombes JS. Astaxanthin: a potential therapeutic agent in cardiovascular disease. Marine Drugs. 2011;9(3):447-465.
2. Kidd P. Astaxanthin, cell membrane nutrient with diverse clinical benefits and anti-aging potential. Alternative Medicine Review. 2011;16(4):355-364.
3. Lyons NM, O'Brien NM. Modulatory effects of an algal extract containing astaxanthin on UVA-irradiated cells in culture. Journal of Dermatological Science. 2002;30(1):73-84.
4. Padayatty SJ, Katz A, Wang Y, et al. Vitamin C as an antioxidant: evaluation of its role in disease prevention. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. 2003;22(1):18-35.
5. Guerin M, Huntley ME, Olaizola M. Haematococcus astaxanthin: applications for human health and nutrition. Trends in Biotechnology. 2003;21(5):210-216.
6. Camera E, Mastrofrancesco A, Fabbri C, et al. Astaxanthin, canthaxanthin and beta-carotene differently affect UVA-induced oxidative damage and expression of oxidative stress-responsive enzymes. Experimental Dermatology. 2009;18(3):222-231.