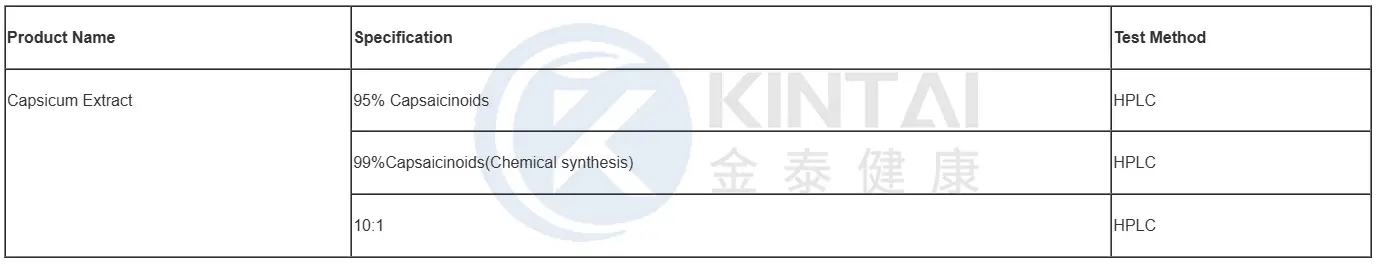
Capsaicin Powder
Specification: 95%98% Capsaicinoids
Test Method: HPLC
Appearance: White crystalline powder
Certifications: ISO, HACCP, HALAL, KOSHER, Technical Invention Patent Certificate
MOQ: 1KG
Sample: Free sample available
Production Capacity: 2000KG/month
Delivery Time: Delivery within one day from warehouse
Shelf Life: Two years
Payment: Multiple terms acceptable like T/T, Paypal,Alipay
Company Advantage:Kintai mainly focuses on the production of high content plant extracts and pharmaceutical intermediates all the year round.
- Fast Delievery
- Quality Assurance
- 24/7 Customer Service
Product Introduction
Capsaicin Powder Manufacturers and Suppliers
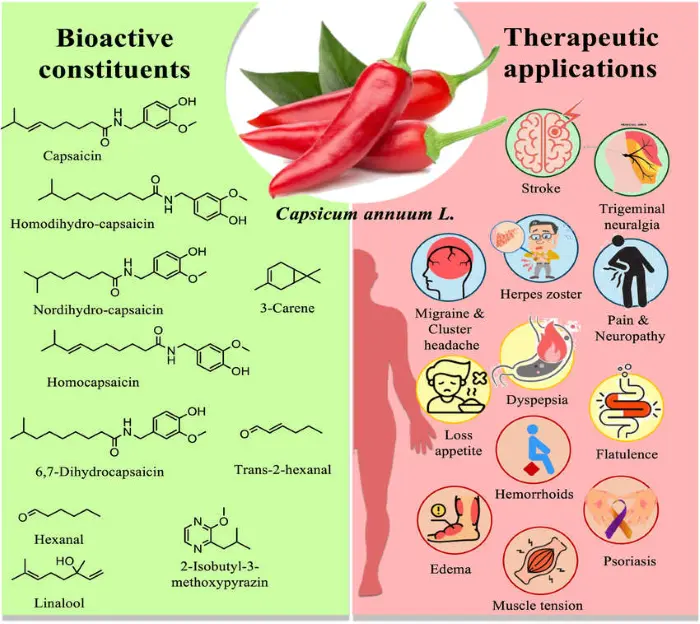
Capsaicin powder is an extremely spicy vanilloid alkaloid with strong irritation. It is the spicy ingredient in chili peppers and the source of the medicinal ingredients in chili peppers. Healthkintai® is a plant extract factory that produces capsaicin, we are both a manufacturer and supplier. If you require high-quality capsaicin powder, please feel free to contact us at info@kintaibio.com.
Other specifications can be customized, contact us now>>>

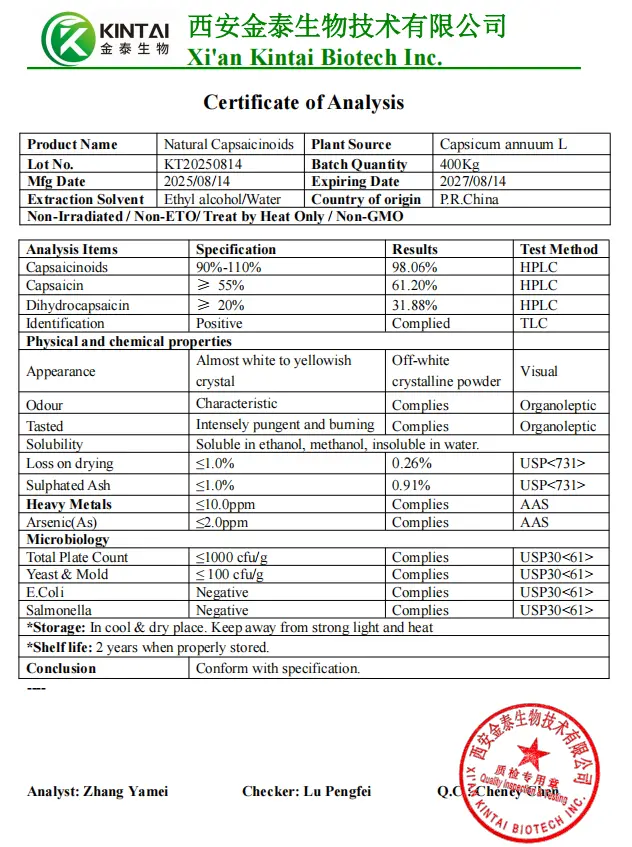
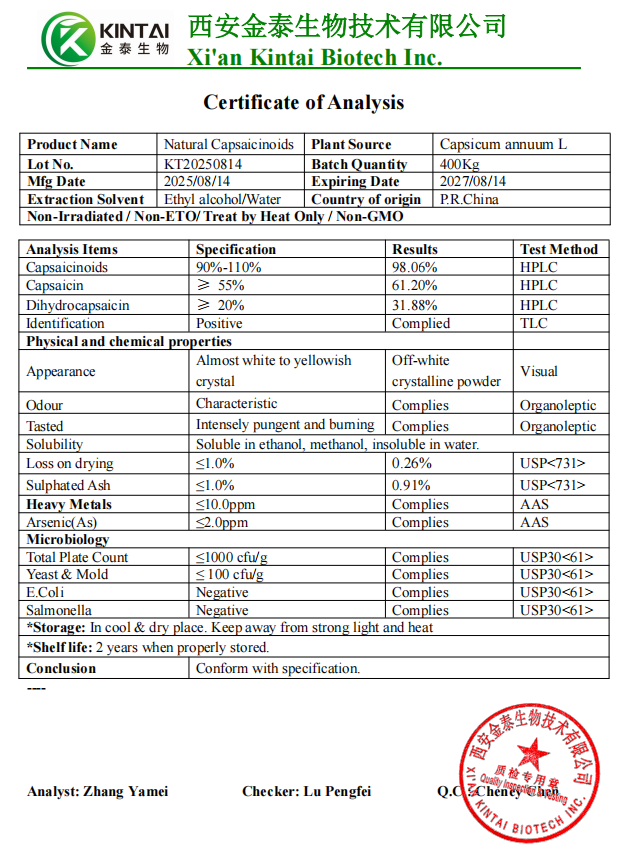
Healthkintai® Capsaicin Powder COA
How does Capsaicin work?
Capsaicin primarily produces its unique spiciness and burning sensation by acting on an ion channel in the human body called TRPV1 (Transient Receptor Potential Vanillin Subtype 1). TRPV1 is essentially a pain and heat receptor, normally activated by high temperatures (>43°C) or acidic environments, sending a warning signal of overheating or injury to the brain. Capsaicin specifically and directly binds to and activates TRPV1 channels, causing an influx of calcium and sodium ions, triggering the same neural electrical signal, leading the brain to mistakenly perceive contact with a heat source, thus producing a burning sensation.
Prolonged or repeated exposure to capsaicin can lead to TRPV1 receptor desensitization (i.e., reduced reactivity), making nerve endings temporarily insensitive to capsaicin or heat stimulation. This mechanism is also used in some analgesics. Furthermore, capsaicin can promote the release of substances such as endorphins, producing a feeling of pleasure. Therefore, the spiciness of capsaicin is not a real physical burn, but rather a deceptive chemical stimulus to the nervous system.
Lidocaine vs Capsaicin
Capsaicin and lidocaine are two analgesics with diametrically opposed mechanisms. Lidocaine is a classic local anesthetic that works by reversibly blocking voltage-gated sodium ion channels on nerve cell membranes, preventing the generation and conduction of nerve impulses, thus achieving rapid and complete local sensory loss (numbness). It is mainly used in minor surgical procedures, dental procedures, and wound suturing where immediate and complete pain blockage is required.
In contrast, capsaicin's action is complex and unique: it specifically activates TRPV1 receptors (an ion channel associated with heat and pain) on sensory neurons, initially causing a burning sensation and pain; however, continuous or high-concentration use leads to TRPV1 receptor desensitization and depletion of pain-causing substances (such as substance P) in nerve endings, resulting in a long-lasting analgesic effect, particularly suitable for the long-term management of neuropathic pain (such as postherpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy) and chronic muscle and joint pain.
Choosing capsaicin for chronic pain management has unique advantages. Unlike lidocaine, capsaicin has a more selective and modulatory effect. It doesn't simply paralyze nerves, but rather reduces the sensitivity of pain nerves to harmful stimuli through a desensitization mechanism, without affecting normal nerve functions such as touch and proprioception. This differentiated effect causes less disruption to the patient's daily life. More importantly, its analgesic effect can last for weeks to months after treatment, providing long-lasting relief and avoiding the need for frequent medication.
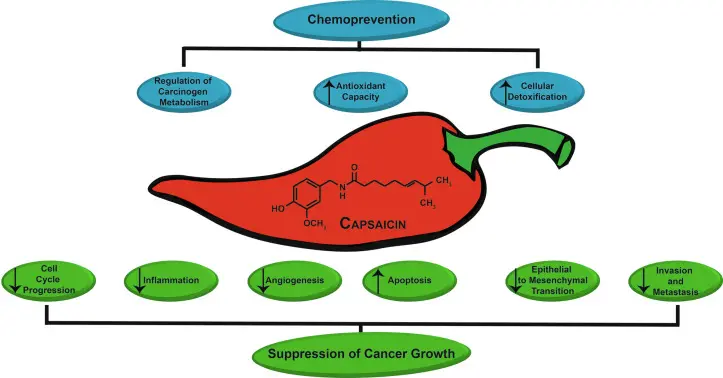
Capsaicin Powder Benefits
Capsaicin for blood pressure
Short-term acute intake of high doses of Capsaicin powder can activate TRPV1 receptors in sensory nerve endings, triggering a transient excitation of the sympathetic nervous system, which may lead to an increased heart rate and a transient, mild increase in blood pressure. However, long-term, regular intake of capsaicin has been confirmed by multiple studies to have a clear blood pressure-lowering benefit. People who habitually consume chili peppers tend to have a lower incidence of hypertension and related cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Therefore, although there may be an initial irritant reaction, capsaicin is a potential cardiovascular protective factor in the long term.

Capsaicin for neuropathy
Capsaicin is an important and uniquely mechanistic nonpharmacological option for treating neuropathic pain. It initially causes a burning sensation by acting on TRPV1 receptors on sensory nerve endings; however, continued use leads to receptor desensitization and depletion of pain neurotransmitters (such as substance P), thus selectively reducing the transmission of pain signals without affecting tactile and motor function. Clinical practice and guidelines recommend, especially high-concentration (8%) capsaicin patches, which have been shown to significantly relieve localized burning and tingling pain caused by postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, etc., with the analgesic effect lasting up to 3 months after a single application.
Capsaicin for osteoarthritis
Capsaicin is an effective local therapy for treating pain associated with osteoarthritis. It works by acting on TRPV1 receptors on the sensory nerve endings in the skin, initially causing a transient warming sensation, but subsequently leading to the depletion of pain neurotransmitters (such as substance P) and receptor desensitization, thereby selectively blocking the transmission of local pain signals. Its advantage lies in its direct action on the painful area, avoiding the systemic side effects of oral analgesics (such as gastrointestinal or cardiovascular risks), providing patients, especially those intolerant to traditional medications, with a safe adjunctive or alternative analgesic option.
Capsaicin Powder Uses
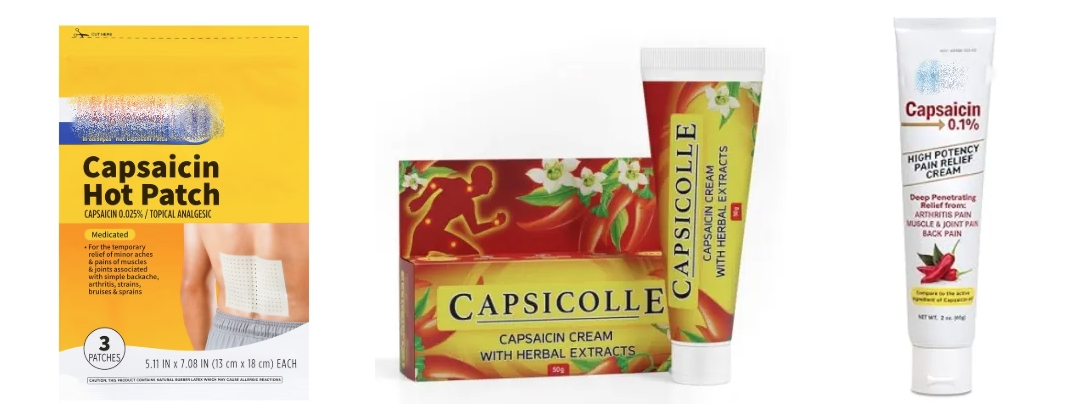
Capsaicin Cream/Gels/Patch
Capsaicin powder is used in topical formulations primarily in the form of patches, creams, and gels. Depending on the concentration and dosage form, it is designed to serve different clinical needs. Low-concentration (typically 0.025% to 0.1%) over-the-counter creams or gels are suitable for repeated daily application to relieve mild muscle and joint pain; their effects are mild but require several days of continuous use to become effective. In contrast, high-concentration (8%) capsaicin patches are prescription medications and represent a revolutionary treatment option. These patches are specifically designed to treat severe neuropathic pain.

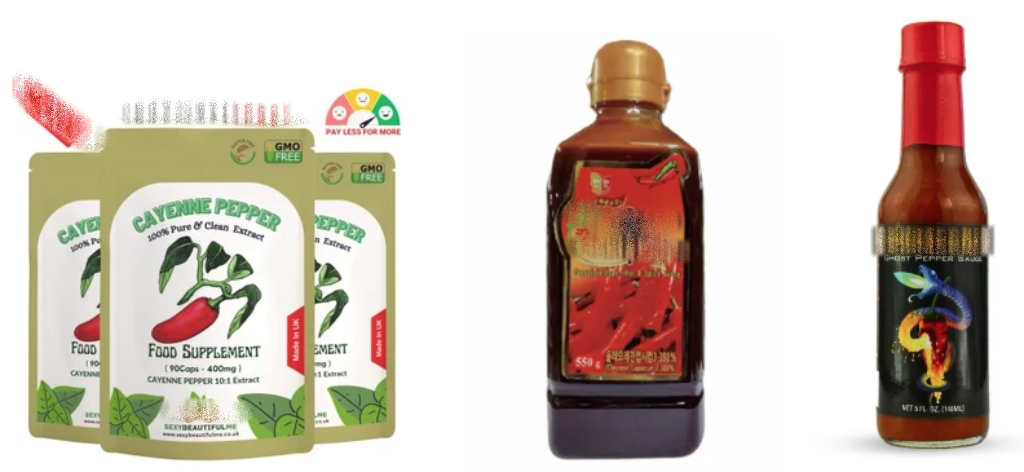
Capsaicin extract for foods
Capsaicin is a multifunctional core ingredient in the food industry, with applications far exceeding simply providing spiciness. Firstly, it is crucial for flavor building and grading; by precisely controlling capsaicin content, manufacturers can create a full range of seasonings from mild to extra spicy, meeting diverse market demands. Secondly, as a natural food preservative, Capsaicin powder's antibacterial and antioxidant properties help extend the shelf life of certain products. More importantly, it is used as a functional food ingredient, catering to consumers' desire for stimulating foods with potential health benefits.

Side Effects of Capsaicin
The side effects of capsaicin mainly stem from its stimulating activation of TRPV1 receptors on sensory nerves, typically local and temporary. The most common reactions are intense local burning, redness, and stinging, especially with initial use or improper use of high-concentration products. Contact with eyes, oral mucosa, or broken skin can cause severe pain and inflammation. Prolonged or excessive topical use (such as high-concentration patches) may lead to decreased skin sensitivity or temporary peeling at the treated area.
Where to buy Capsaicin Powder?
Healthkintai®'s capsaicin products possess comprehensive core competitiveness. We carefully select premium chili varieties to ensure the purity and high capsaicin content of the raw materials. We can flexibly provide customized products with different purities, dosage forms (powder, liquid, crystals), and Scoville Heat Units (SHU) according to customer needs. Our factory strictly adheres to international standards and holds ISO, HACCP, Kosher, Halal, and other authoritative certifications. As a supplier with its own production plant, we effectively control costs through large-scale production and optimized supply chain management, allowing us to offer customers highly competitive prices.To find Capsaicin Powder for sale,contact us at info@kintaibio.com.

Send Inquiry


_1769408078542.jpg)