Is Dihydromyricetin Safe To Use?
2025-06-17 16:09:00
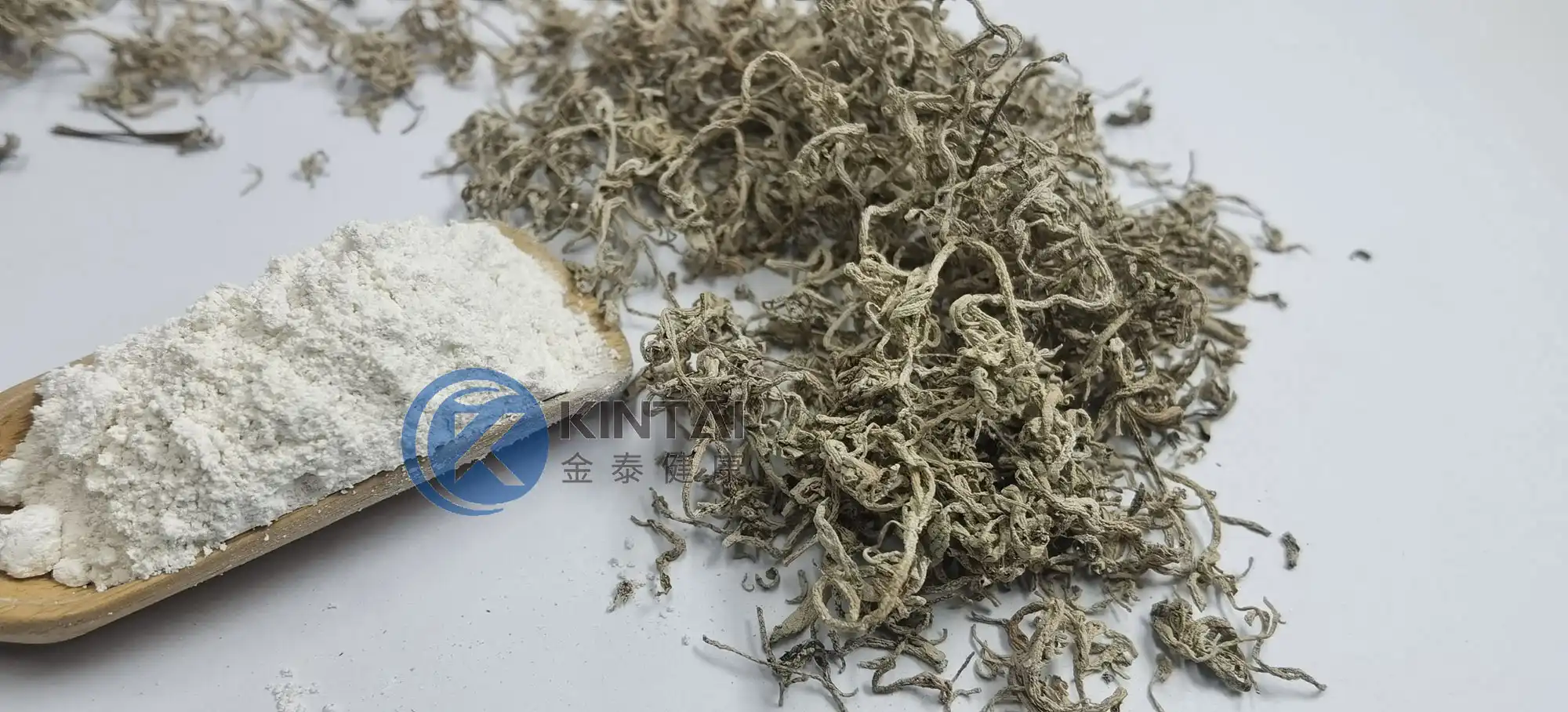
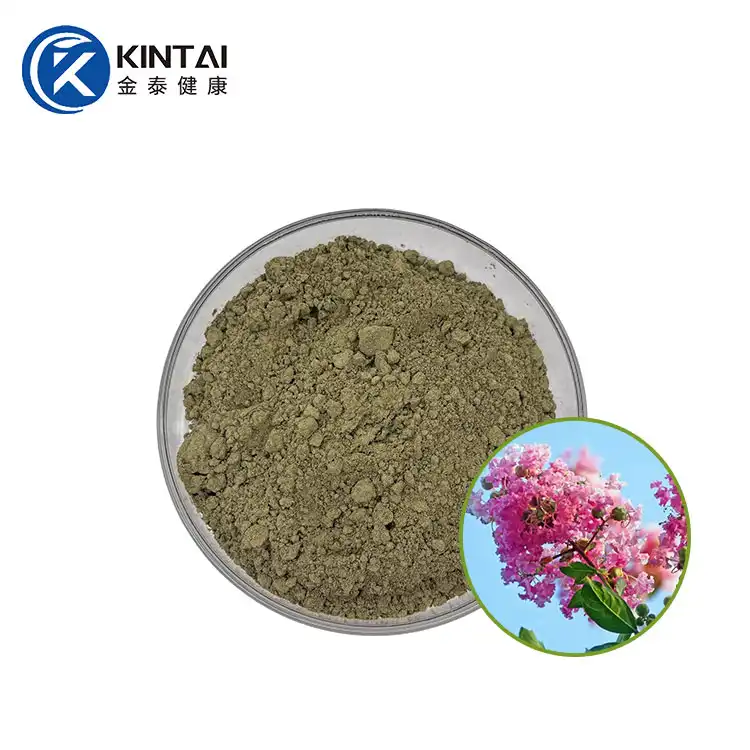
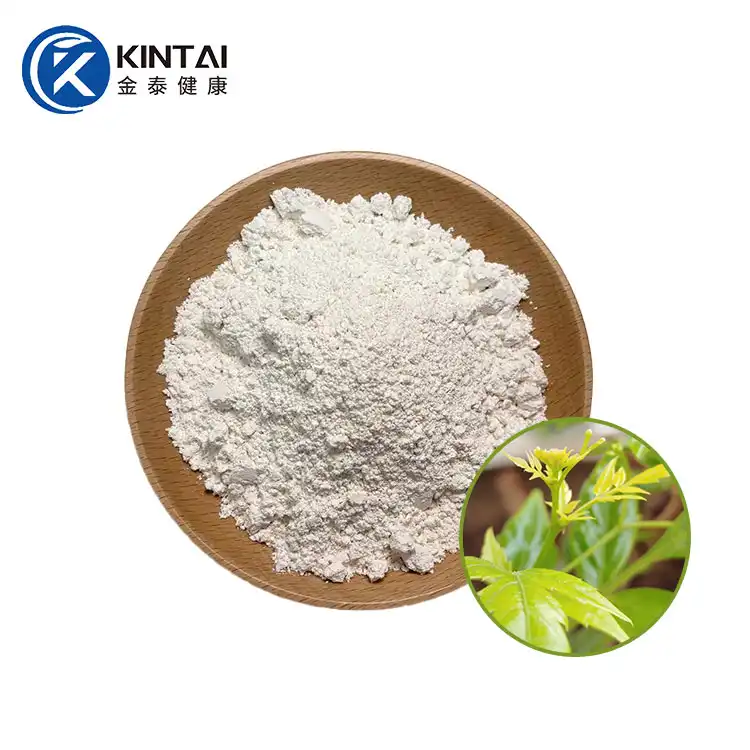
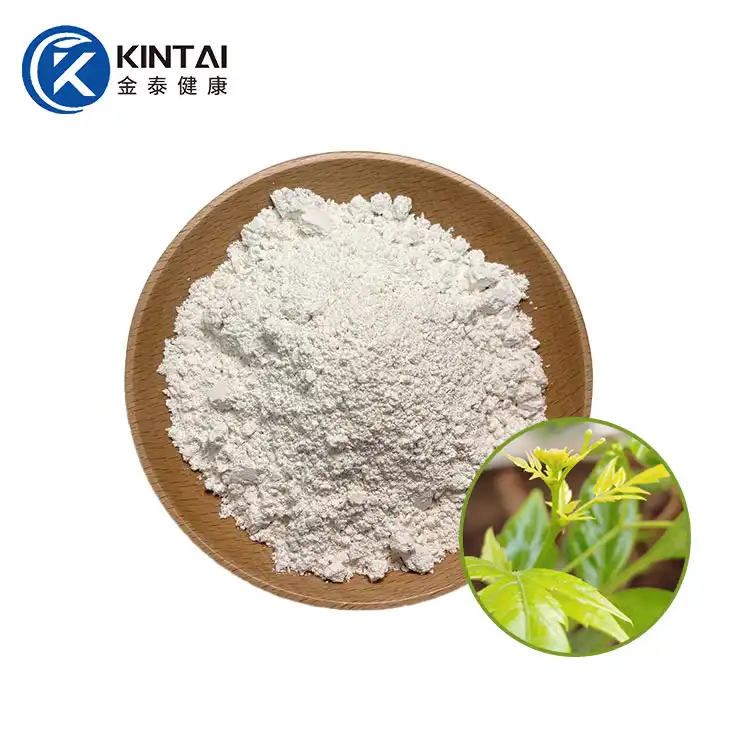
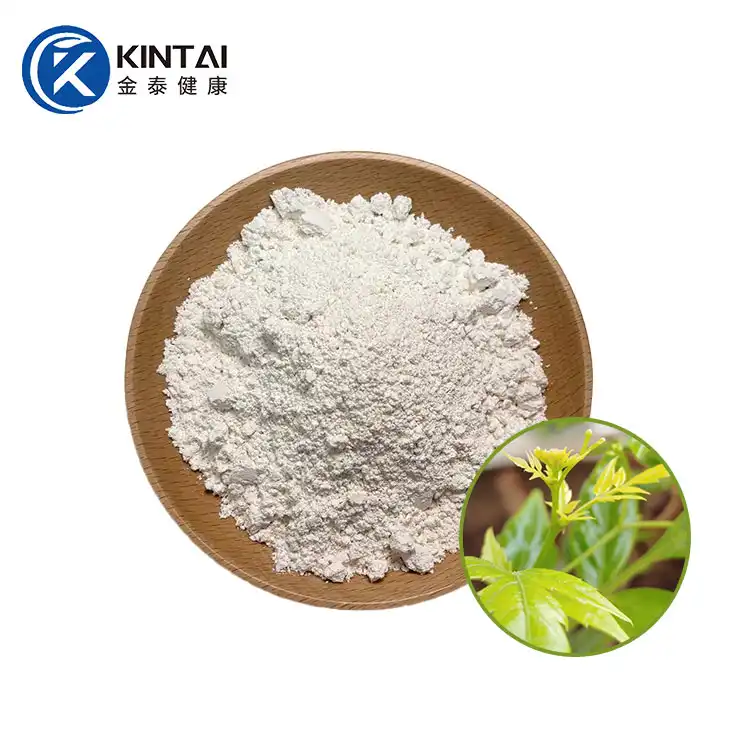
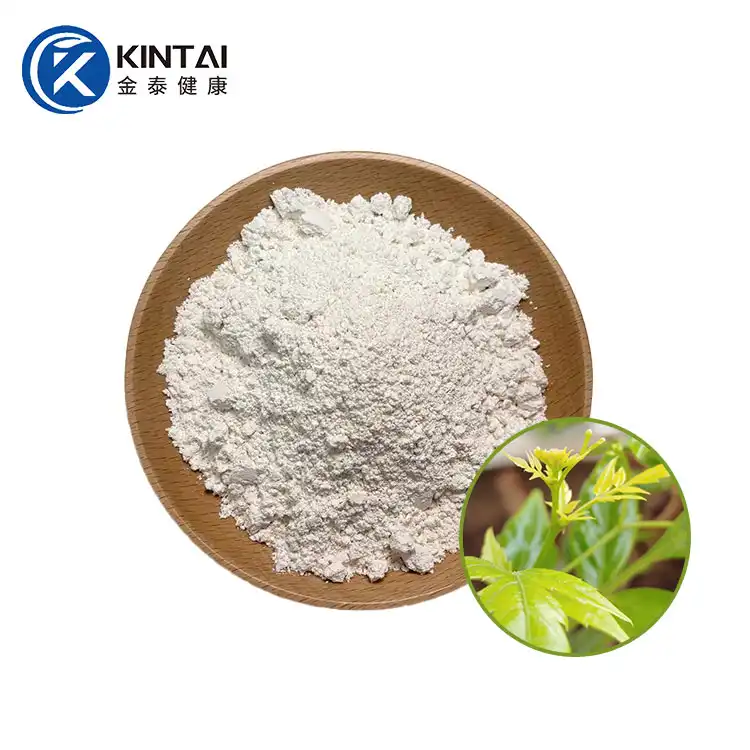
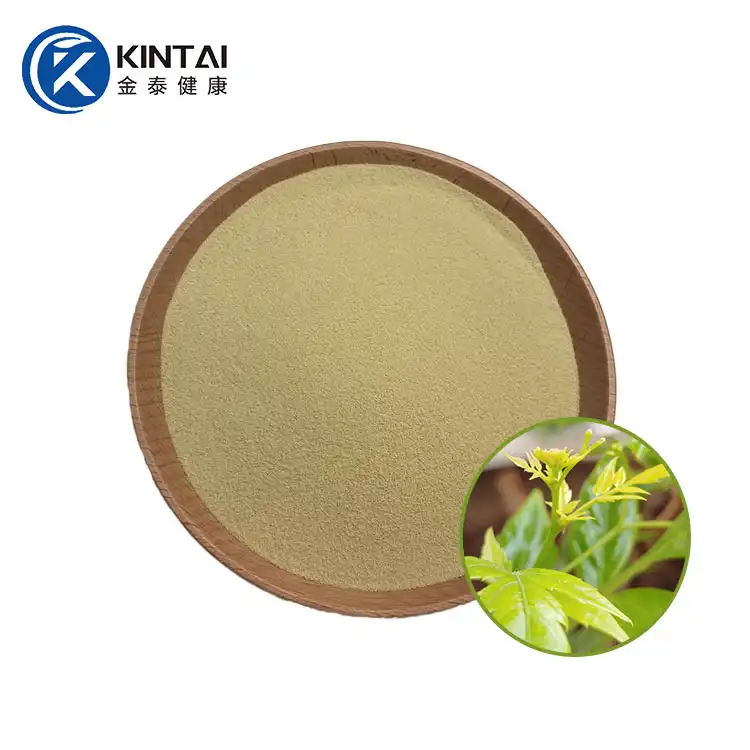
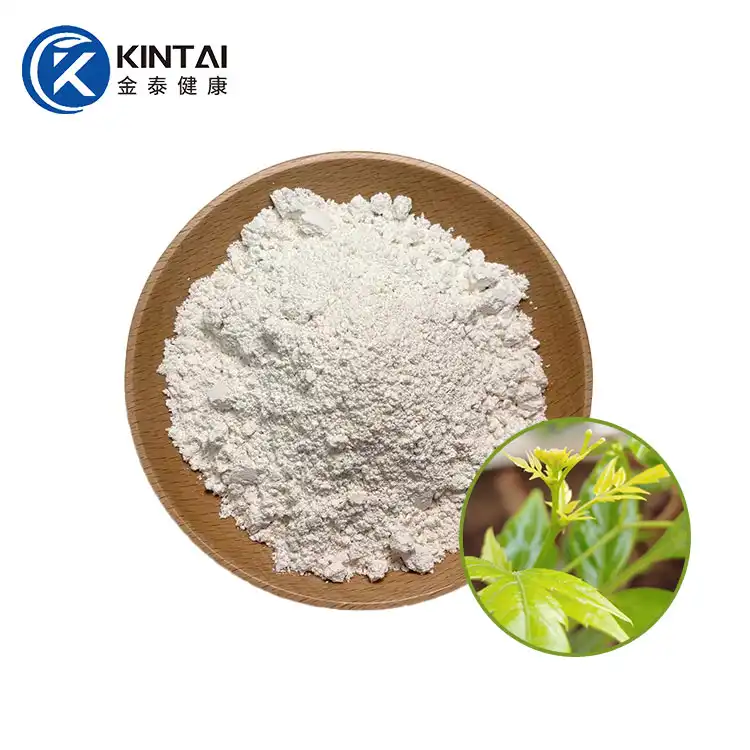
Dihydromyricetin (DMY or DHM), also known as ampelopsin (AMP) and ampelopsin, is a dihydroflavonol flavonoid compound. In 1940, it was first isolated from the leaves of the neem-leaved grape of the genus Ampelopsin. Previous studies have confirmed that DHM has multiple pharmacological effects such as antioxidant, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, alcohol detoxification and liver protection, anti-pathogenic microorganisms and blood lipid regulation. In addition, DMY also has biological activities such as anti-hypertension, inhibition of thrombosis in the body, and hypoglycemia.
Kintai is a Chinese factory specializing in the production of dihydromyricetin powder. We provide high-quality 98% dihydromyricelin powder and 30% water-soluble DHM powder. Please contact us if you need to purchase.
1. Anti-tumor effects
Dihydromyricetin can inhibit the proliferation of liver cancer cells, breast cancer cells, prostate cancer cells and bladder cancer cells, and promote apoptosis of various tumor cells. Its mechanism of action is related to inducing apoptosis of tumor cells, blocking the cell cycle of tumor cells, inducing autophagy of tumor cells, and inhibiting the invasion of tumor cells.
2. Antioxidant
Free radicals are highly active in organisms, with unstable structures, and can react with neighboring proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. The resulting oxidative stress is involved in many diseases, such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, and diabetes, and is also involved in the aging process. Dihydromyricetin has strong antioxidant activity, which is related to its many pharmacological effects and is also the basis for its application in animal husbandry as a safe, residue-free food additive.
3. Anti-inflammatory
Dihydromyricetin can significantly inhibit the release of NO and inflammatory factors such as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) from RAW264.7 cells induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and it is dose-dependent; it can effectively inhibit the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) induced by LPS, and the mechanism is closely related to the inhibition of IκB kinase phosphorylation, IκB phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of nuclear transcription factor-κB (NF-κB).
Dihydromyricetin can reduce the amount of triglycerides (TG), reduce fatty degeneration of liver cells, and has a significant protective effect against alcoholic liver damage. This effect may be achieved by scavenging free radicals, improving the antioxidant capacity of liver cells, and inhibiting membrane lipid peroxidation caused by ethanol.
5. Hypoglycemic
Dihydromyricetin can inhibit the activity of diabetes-related enzymes. Aldose reductase is the key rate-limiting enzyme in the polyol pathway of sugar metabolism, which is closely related to diabetic complications. Dihydromyricetin can inhibit the activity of aldose reductase in a concentration-dependent manner, thus having a potential hypoglycemic effect.
6. Anti-pathogenic microorganisms
Dihydromyricetin has strong inhibitory activity against Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus and other bacteria, and the antibacterial effect is strongest in an environment of pH 3-4, but the inhibitory effect on fungi is not obvious; Dihydromyricetin has a significant inhibitory effect on DHBV-DNA in the serum of ducks with hepatitis B, and there is no rebound phenomenon 3 days after stopping the drug.
7. Other effects
Dihydromyricetin has a wide range of pharmacological activities. In addition to its anti-tumor, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects, it also exhibits certain biological activities such as anti-fatigue, anti-thrombosis, and lipid regulation.
Xu Jingjuan et al. conducted an acute toxicity test on rats with dihydromyricetin (5.0 g/kg) in accordance with the requirements of the Technical Specifications for Acute Toxicity Tests for Inspection and Evaluation of Health Foods. During the observation period, no abnormalities were found in the skin, mucous membranes, fur color, eyes, respiration, circulation, autonomic activity, central nervous system, and behavioral performance of the rats. The body weight of the rats did not change significantly, and no animals died during the test period, indicating that dihydromyricetin is very low in toxicity.
The results of the acute toxicity test of the ethanol extract of rattan tea also showed that after the rats were given 10.0 g/kg of ethanol extract of rattan tea (the amount of dihydromyricetin was determined to be 70%), there was no significant change in the acute toxicity evaluation indicators, indicating that the snake grape (dihydromyricetin tea) has good food safety.
As a professional plant extract manufacturer, Jintai has been providing high-quality dihydromyricetin powder for many years. Whether you are using it for medicine, food or cosmetics, we can provide you with the quality you need. We have always insisted on complete certificates, stable supply, consistent quality and thoughtful service. Please contact info@kintaibio.com for detailed information.